Depositors to get max Tk 2 lakh on bank liquidation
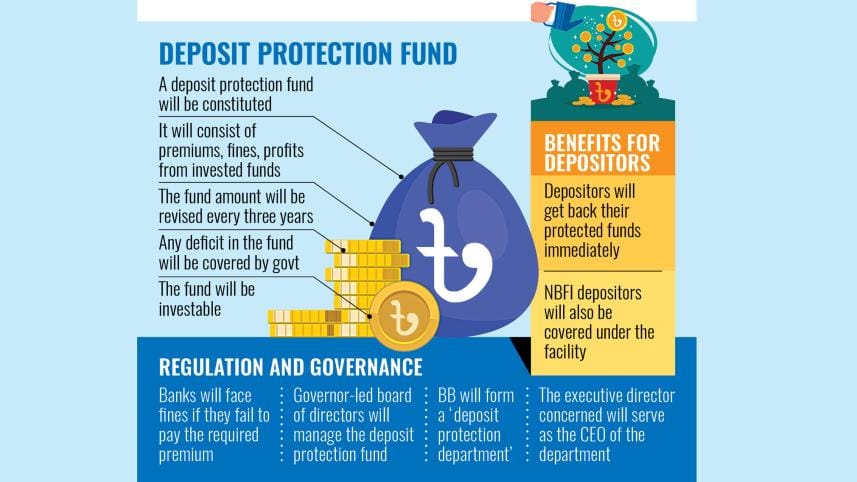
The Bangladesh Bank (BB) has drafted a Deposit Protection Ordinance, proposing a maximum payout of Tk 2 lakh per depositor if a bank undergoes liquidation. The limit will be reviewed every three years.
The draft, now open for public feedback, maps out the establishment of a Deposit Protection Authority within the central bank, which will oversee a separate fund maintained through premiums from financial institutions.
Depositors surpassing the protection limit must claim the excess through the liquidator.
The ordinance also details a seven-day payout window for secured deposits and tax exemptions for the fund's earnings. The central bank may impose penalties on institutions failing to pay premiums on time.
Earlier, central bank Governor Ahsan H Mansur hinted at the introduction of the ordinance to ensure depositor protection.
The ordinance will replace the Bank Deposit Insurance Act-2000, under which the maximum payout is Tk 1 lakh.
According to the draft ordinance, the government will establish a deposit protection system for its implementation, with the BB designated as the Deposit Protection Authority.
"The responsibilities of the authority will be separate and independent from the Bangladesh Bank's regular responsibilities, such as regulatory, supervisory, and resolution-related functions," says the draft.
To ensure the effective exercise of its powers and responsibilities, the central bank will create a separate division within its organisational structure, called the "Deposit Protection Division".
Decisions regarding the deposit protection system will be made by a board of directors comprising seven members, with the BB governor as the chairman.
The board will determine the maximum limit of protected deposits at least once every three years and oversee regulations, by-laws, investment policies, and risk-based premium rates.
It will also allocate funds to support bank resolutions.
Deposit protection fund
Under the ordinance, the central bank will establish a deposit protection fund, maintained through a separate account.
The fund will comprise initial, annual risk-based, and special premiums received from banks; penalties collected from member institutions; profits earned from investments; adjusted funds from liquidated banks; and other unconditional funds designated for payment.
Primarily, the fund will be used to pay secured deposits in the event of a bank's dissolution, though it may also provide financial assistance for bank resolution.
In the case of a fund deficit, the BB will have the authority to collect special premiums from member institutions, seek unconditional financial assistance from the government or other sources, or secure government loans.
Besides, the central bank will establish a separate fund for depositors of non-bank financial institutions.
The draft ordinance says that, regardless of the Income Tax Act, 2023, the Business Profits Act, 1947, or any other existing tax laws, no income tax, surtax, or business profits tax shall be applicable to the income, profits, or receipts of the Deposit Protection Fund.
Moreover, if a member institution fails to pay the prescribed premium within the stipulated timeframe, the BB will deduct the corresponding amount from the institution's current account and deposit it into the relevant account of the Deposit Protection Fund.
The central bank may also impose a penalty on overdue premiums, applying an interest rate equivalent to the higher of Bangladesh Government Treasury Bonds or Treasury Bills.




 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
Comments