Antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance threatens to collapse our health system
This crisis is pushing us dangerously close to a pre-antibiotic era.
12 December 2025, 03:00 AM
The danger of antibiotic resistance must not be ignored anymore
Latest official data raise serious concerns.
25 November 2025, 13:00 PM
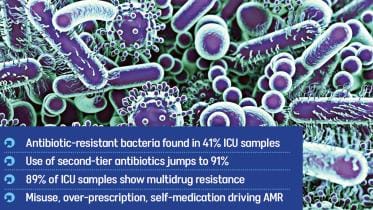
Antibiotics not working on 4 in 10 ICU patients
Four in every 10 patients admitted to intensive care units (ICUs) are not responding to available antibiotics due to their overuse and misuse, according to government data released yesterday, raising fresh concerns about the growing threat of antibiotic resistance.
24 November 2025, 18:00 PM
Unveiling the struggles of Bangladesh’s pharmaceutical representatives
Bangladesh’s pharmaceutical industry is marred by exploitative practices that push employees to their limits and compromise ethical standards.
19 June 2024, 10:00 AM
Antimicrobial resistance: The overlooked pandemic
A recent study covering 204 countries shows a 46 percent increase (of daily doses per 1,000 people) in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2018. South Asia is among the regions where antibiotic resistance continues unabated for all ages.
11 February 2023, 15:00 PM
How do we solve antibiotic resistance?
.Antibiotic resistance threatens to take us back to a time before penicillin when the majority of deaths were caused by infections. What are we doing to solve the crisis?.Since antibiotics were introduced to the world in the mid-20th century, deaths attributable to infections dropped
15 January 2023, 03:51 AM
5 topics to get you updated on Nov 25: Another BNP rally, more World Cup and stories on VAW
Happy weekend to everyone who is celebrating. If you are busy catching up on all the household chores you missed throughout the week and did not get a chance to glance through the paper then give us a few minutes to get you all updated!
25 November 2022, 11:28 AM
Antibiotic resistance: Edging closer to a health calamity
Most of the clinically important antibiotics are now less effective at killing disease-causing bacteria than the last few years, shows the latest surveillance data of the government.
25 November 2022, 01:00 AM
Fears grow over increased antibiotic resistance
More than 6,000 deaths a year could be caused by a 30% fall in the effectiveness of antibiotics in the US, a report in The Lancet suggests.
16 October 2015, 12:16 PM
Antibiotic resistance at an alarming level
The WHO has made an ominous forecast: an estimated 10 million deaths per year and a global gross domestic product 2-3 percent less than woluld otherwise be by 2050.
7 September 2015, 18:00 PM