The Digital Transformation of Bangladesh’s Financial Landscape
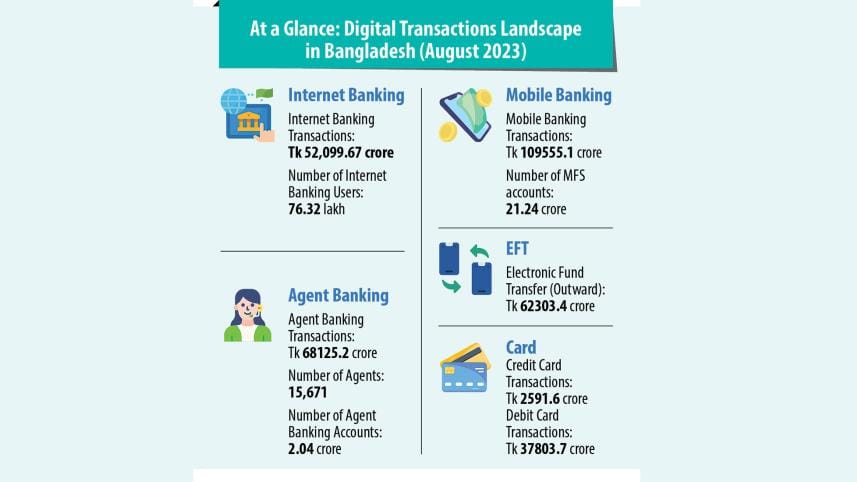
Bangladesh's financial sector is advancing rapidly in digitization, unveiling a robust digital infrastructure and innovative products. This development enables millions to access financial services while enhancing service delivery efficiency.
In a remarkable stride toward modernization, the sector is undergoing a digital revolution aiming to enhance financial inclusion, streamline services, and propel the nation into a digital future.
Bangladesh's financial institutions have made significant investments in upgrading their digital infrastructure to meet the demands of a rapidly evolving market. The implementation of advanced technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing has strengthened the sector's resilience and efficiency.
The Bangladesh Bank, the central bank of the country, has also played a role in fostering this digitization wave. Its initiatives include the development of a secure and robust digital payment infrastructure, facilitating seamless transactions and reducing dependency on traditional banking channels. A host of innovative products has been introduced to cater to the diverse needs of consumers and businesses. mobile financial services, digital wallets, digital nano loans, and online payment platforms have become integral parts of everyday financial transactions.
These tools not only provide convenience but also promote financial inclusion by reaching the unbanked population. The Bangladesh Financial Intelligence Unit (BFIU) issued a comprehensive guideline for Electronic Know Your Customer (eKYC) in 2020, revolutionizing the account opening process for any bank or financial service provider (FSP). This innovative approach allows individuals to initiate the account creation or digital wallet setup entirely through a digital framework.
Under this streamlined eKYC process, a customer engages in a straightforward procedure by capturing images of the front and back of their National ID (NID) card, along with a selfie. Subsequently, the bank or FSP utilizes advanced technology to meticulously verify the authenticity of the NID and the profile photo. This verification process is conducted against the national election commission database, ensuring the accuracy and legitimacy of the provided information.
This digitized KYC method not only expedites the account opening process but also enhances security measures by leveraging technological advancements, according to industry experts.
The financial institutions in Bangladesh have invested heavily in robust core banking systems, central software that enables financial institutions to manage and streamline key banking operations that form the backbone of their activities. These systems integrate various banking processes, including account management, transactions, and customer relationship management, according to industry experts. Some forward-thinking banks and financial institutions have started using blockchain technology for secure and transparent financial transactions. Blockchain enhances security, reduces fraud, and streamlines processes like cross-border payments. For scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, some are adopting cloud infrastructure. Financial institutions are migrating some of their operations to cloud-based platforms to improve accessibility and reduce dependence on physical infrastructure. Many banks have already struck deals with some of the cloud service providers.
Given the increasing threats in the digital space, financial institutions prioritize robust cybersecurity measures. This includes firewalls, encryption tools, and threat detection systems to safeguard sensitive financial data. Institutions are also investing in data analytics tools and artificial intelligence to derive insights from large datasets, enabling them to be more efficient in risk management, fraud detection, and personalized customer experiences.

Cash recycling machines (CRMs), set up by banks in Bangladesh to help clients deposit, withdraw, and transfer money instantly, almost doubled in the last financial year. As of September 2023, banks installed 3717 such machines, according to data from the Bangladesh Bank. Five years ago, the number of such machines stood at only 219. Banks have been increasingly installing CRMs as they offer a range of core banking services, reducing customers' reliance on branches and giving them more freedom to carry out financial transactions whenever they want since the machines operate round the clock.
A CRM can accept cash, count the notes, authenticate them, and credit the amount to accounts on a real-time basis, helping banks do away with the manual labor needed to provide the service.
It allows users to deposit and transfer funds to other accounts as well. CRMs can establish a crucial link by leveraging customer data to enhance personalized experiences. Integrated CRM systems analyze digital interactions, providing insights for targeted services, streamlined operations, and proactive issue resolution. This synergy fosters a customer-centric approach, optimizing the digital banking experience and fostering lasting relationships.
On the product side, banks are offering a variety of digital banking products to cater to the evolving needs of their customers. Most banks in Bangladesh offer mobile banking apps that allow customers to perform a range of transactions, including fund transfers, bill payments, and mobile recharge, all from their smartphones. Online banking platforms of banks enable customers to manage their accounts, view transaction histories, pay bills, and conduct various financial transactions through secure web interfaces. Some banks issue debit and credit cards equipped with digital features for online transactions, both domestic and international. These cards are often integrated with popular payment networks like Visa and MasterCard.
The Bangladesh Bank has already commenced a campaign to popularize an interoperable QR code across the capital city to bring millions of small businesses, such as street vendors and lower-income groups, under the digital transaction system. The uniform digital payment method, Bangla QR, helps clients pay bills for goods and services through mobile banking applications, mobile financial services (MFS), and payment service providers (PSPs). The central bank's initiative, styled "Cashless Bangladesh," is cost-effective, secure, and card-less and will help promote digital transactions to a large extent in an economy that relies almost entirely on paper currencies and notes to function.
Digital nano loans display a promising prospect thanks to the instant and on-time disbursement of loans. About 1.6 lakh customers have already availed loans from lenders, and the default rate is less than 1 percent, according to the banks. The lenders are disbursing loans ranging from Tk 500 to Tk 50,000 to individual customers at up to 9 percent interest.
Mobile Financial Services (MFS) have played a transformative role in revolutionizing digital financial services in Bangladesh. Platforms like bKash and Nagad have enabled widespread financial inclusion by providing accessible and convenient digital services, such as mobile money transfers, bill payments, and even savings. MFS has empowered individuals, particularly in rural areas, who previously lacked access to traditional banking. This revolution has accelerated economic activities, reduced reliance on cash, and enhanced financial literacy, contributing significantly to Bangladesh's digital financial landscape.
bKash has been a trailblazer in introducing innovative digital financial services in Bangladesh. The platform offers a wide range of bill payment services, including utility bills, internet bills, and mobile phone recharges. This convenience has simplified everyday financial transactions for users. It has expanded its services to enable users to make payments at various merchants, allowing for cashless transactions at shops, restaurants, and other retail outlets. bKash has collaborated with international partners to facilitate cross-border remittances, providing a streamlined and cost-effective way for Bangladeshi expatriates to send money home. bKash pioneered digital nano loans and savings accounts through MFS, promoting financial inclusion and allowing users to access credit and savings services.
Nagad's disruptive innovations have also ignited a digital financial revolution in Bangladesh, transforming the landscape with groundbreaking solutions that promise to redefine how individuals engage with and experience financial services in Bangladesh.
The disruptive MFS carrier first shook the financial industry by introducing a simplified account opening process in the form of Electric Know Your Customer (e-KYC). Such groundbreaking innovation brought an end to cumbersome paperwork. As a result, customers do not need to find an agent to open an account, thus saving a lot of time and money. Other MFS providers and banks adopted e-KYC, which also helped them reduce their costs of doing business. Nagad now has a customer base of 8.5 crore with its daily transactions standing at BDT 1,300 crore on average.
According to industry experts, there are challenges in Bangladesh's digital financial sector that include cybersecurity threats, limited digital literacy, and infrastructure gaps.
"Weak technological infrastructure, lack of widespread internet connections, fear of digital security and data privacy, poor digital literacy, and unbanked populations are the key challenges for providing digital banking services," HM Mostafizur Rahaman, head of retail business at Dhaka Bank.
see page J2



 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
Comments